CSS basics
Updated:
✒ Reference: CSS Tutorial by W3Schools
What is CSS?
-
Cascading Style Sheets: The language used to style a Web page
-
Defines style for HTML elements, including the design, layout, and variations for different devices and screen sizes
-
Can control the layout of multiple web pages at once
-
Syntax
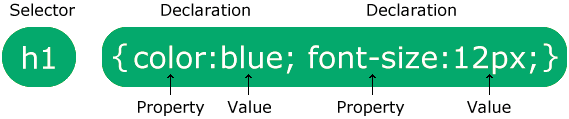
- Selector: points to the HTML that is styled
- Declaration block: contains one or more declarations separated by semicolons, surrounded by curly braces
- Each declaration includes a CSS property name and a value, separated by a colon
/* All <h1> elements will be center-aligned, with a red text color. */
h1 {
color: red;
text-align: center;
}
Inserting CSS
- There are three ways: external CSS, internal CSS, and inline CSS.
- When there is more than one style specified for an HTML element, with the priority of:
- Inline style (in the HTML element)
- External and internal style (in the head section)
- Browser default
-
External CSS
-
The HTML page must include a reference to the external style sheet file inside the
<link>element, inside the head section. -
Within head, there should be:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="mystyle.css"> -
The external CSS file should not contain any HTML tags, and must be saved with a
.cssextension.
-
-
Internal CSS
-
Internal styles are defined within the
<style>element, inside the head section. -
Within head, there should be:
<style>css code here</style>
-
-
Inline CSS
-
Inline style is used to apply a unique style for a single element.
-
An inline style loses the advantage of a style sheet, mixing the content with the presentation.
-
A style attribute is added to the relevant element:
<p style="css code"></p>
-
CSS selectors
Simple selectors
| Selector | Example | Example description |
|---|---|---|
| #id | #firstname | Selects the element with id=”firstname” |
| .class | .intro | Selects all elements with class=”intro” |
| element.class | p.intro | Selects only <p> elements with class=”intro” |
| * | * | Selects all elements |
| element | p | Selects all <p> elements |
| element,element,.. | div, p | Selects all <div> elements and all <p> elements |
Combinator selectors
In CSS, there are four combinators that explain the relationship between the selectors.
- descendant selector (space)
- child selector (>)
- adjacent sibling selector (+)
- general sibling selector (~)
| Selector | Example | Example description |
|---|---|---|
| element element | div p | Selects all <p> elements inside <div> elements |
| element>element | div > p | Selects all <p> elements where the parent is a <div> element |
| element+element | div + p | Selects the first <p> element that are placed immediately after <div> elements |
| element1~element2 | p ~ ul | Selects every <ul> element that are preceded by a <p> element |
/* i.e. Select all <p> elements that are next siblings of <div> elements: */
div ~ p {
background-color: yellow;
}
More selectors
- Pseudo-class selectors (select elements based on a certain state)
- Pseudo-elements selectors (select and style a part of an element)
- Attribute selectors (select elements based on an attribute or attribute value)
CSS pseudo-class
- A pseudo-class is used to define a special state of an element. (style the link when hovered)
- Syntax:
selector:pseudo-class {
property: value;
}
- Anchor pseudo-classes: links can be displayed in different ways according to their state.
<head>
<style>
/* unvisited link */
a:link {
color: red;
}
/* visited link */
a:visited {
color: green;
}
/* mouse over link
a:hover must come after a:link and a:visited. */
a:hover {
color: hotpink;
}
/* selected link
a:active must come after a:hover. */
a:active {
color: blue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>Styling a link depending on state</h2>
<p><a href="link">This is a link</a></p>
</body>
- Pseudo-classes can be combined with HTML classes.
<head>
<style>
a.highlight:hover {
color: #ff0000;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hovering over the first link will change the color</h1>
<p><a class="highlight" href="link1">Highlighted</a></p>
<p><a href="link2">Not highlighted</a></p>
</body>
- Matching a specified element that is a nth child of another element
- Match the first
<p>element:p:first-child - Match the first
<i>element in all<p>elements:p i:first-child - Match all
<i>elements in all first child<p>elements:p:first-child i
- Match the first
CSS pseudo-element
-
A pseudo-element is used to style specified parts of an element. (style the first letter, etc.)
-
Syntax:
selector::pseudo-element {
property: value;
}
- Pseudo-elements can also be combined with HTML classes.
- Multiple pseudo-elements can be combined:
/* The first letter will be red, and the rest of the first line will be blue. */
p::first-letter {
color: #ff0000;
font-size: xx-large;
}
p::first-line {
color: #0000ff;
font-variant: small-caps;
}
| Selector | Example | Example description |
|---|---|---|
| ::after | p::after | Insert something after the content of each <p> element |
| ::before | p::before | Insert something before the content of each <p> element |
| ::first-letter | p::first-letter | Selects the first letter of each <p> element |
| ::first-line | p::first-line | Selects the first line of each <p> element |
| ::marker | ::marker | Selects the markers of list items |
| ::selection | p::selection | Selects the portion of an element that is selected by a user |

Leave a comment